What an AI agent is, how many types of agents are defined in artificial intelligence and what types are most suitable for your business specifics, how to choose and implement an autonomous AI agent, all the answers are in our new blog post.
Today you can hardly find a business that hasn’t yet implemented AI or thought about how this tech can refine their operations. Intelligent image processing, AI-powered product recommendations, smart chatbots, predictive medicine, AI-fueled surveillance — there are different ways how AI changes businesses.
Underpinned by the necessity to rapidly adapt to the constantly changing market trends and ever-increasing customer demands, companies are starting to perfect AI implementations in their business, focusing more and more on Agentic AI. As opposed to earlier AI versions that follow predefined rules, agentic AI performs complex tasks, makes decisions proactively, easily adapts to new information in real time, with minimized or no human intervention.
However, Agentic AI is not a stand-alone tool, but an overarching system that integrates various specialized AI agents. Before getting into the ins and outs of these tech, let’s first explain the AI agent definition.
What AI Agents Are And How They Work
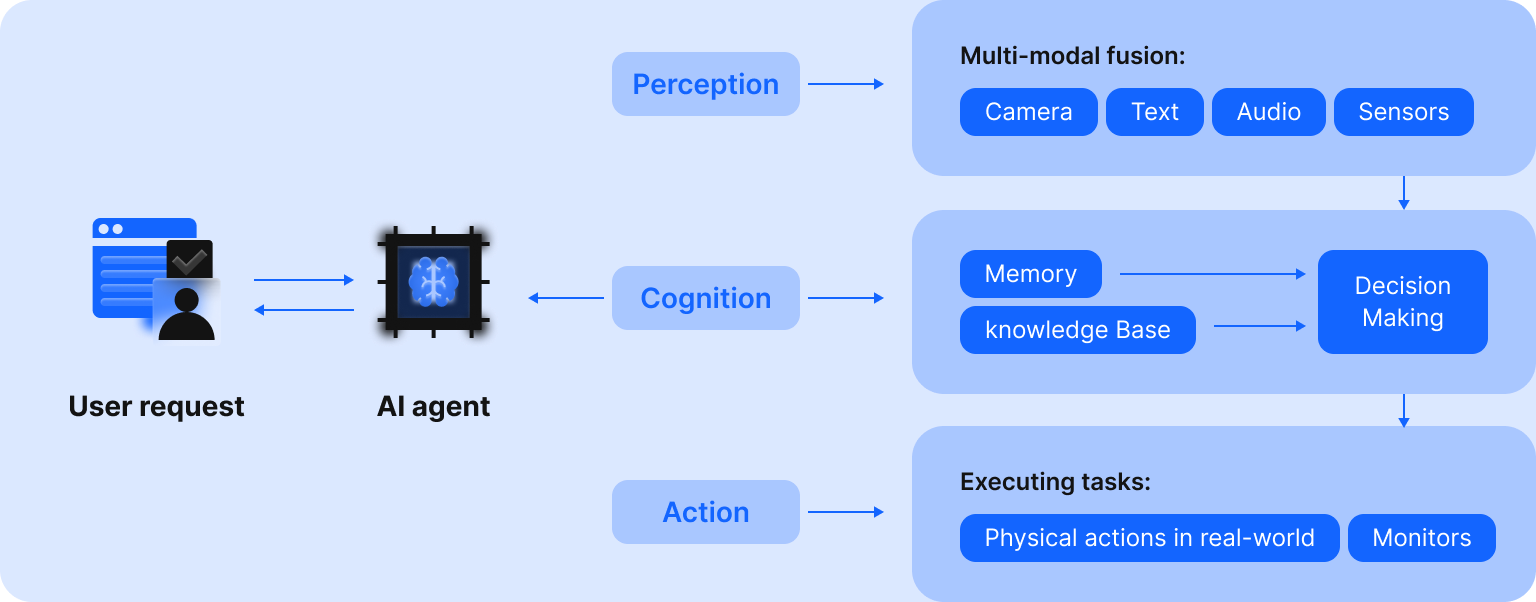
An AI agent is a software entity that understands and perceives its environment via sensors, then processes the collected information, and takes specific actions to achieve its objectives. Operating autonomously or semi-autonomously, an AI agent can be introduced into your business as a digital project manager who works in a continuous cycle through several components:
- Perception means that an AI agent leverages digital “sensors” to collect information from its environment, including your internal databases, domain-specific information, third-party systems and websites, visual / auditory input, etc.
- Reasoning and planning include processing the gathered information via large language models (LLMs). At this stage, AI agents divide the task into smaller parts and define the sequence of actions needed for a desired result. Being the ‘brain’ of an AI agent, LLMs have their limitations, as their knowledge is static. To update an AI agent about constantly-evolving information like your company’s latest policies, market fluctuations, or a patient’s real-time medical data, use the Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technique. This way, your AI agent will convert into a domain expert who leverages dynamic data sources.
- Memory of AI agents can be short-term (for immediate conversations) and long-term (for accumulated knowledge). Through such internal knowledge bases, AI agents retain information from past interactions to better maintain context, make more informed decisions, and learn over time.
- The action module is responsible for performing particular tasks, i.e. digital commands (sending a message, executing code, creating an image) or movements (for a physical robot).
- The learning and refinement module presupposes that AI agents gauge the outcomes of their actions and use feedback loops to enhance their performance and adapt to new use-cases.
- The communication interface allows AI agents to smoothly interact with human users, external systems, or other AI agents. This is needed for understanding a user’s intent to build natural conversations, accessing specialized tools, and building collective intelligence to collaboratively perform complex goals.
Why You Need an AI Agent: Tangible Benefits for Your Business
Knowing what AI agents are, let’s proceed to its business value. Implementing agentic AI is able to bring more bucks for your bang, driving tangible value at any stage of your business growth.
- Higher customer satisfaction. Unlike humans, AI agents are able to work non-stop, ensuring uninterrupted service across different locations and time zones. Such 24/7 availability as well as high precision, accuracy, and consistency slash response times, leading to enhanced customer satisfaction. Moreover, underpinned by advanced data-fueled analytics, AI agents can introduce more personalized marketing, resulting in boosted user engagement and loyalty.
- Process automation. By easily dealing with repetitive routine tasks such as data management, customer inquiries, scheduling, and accounting, AI agents not only notably improve accuracy, but liberate human resources for more creative and strategic activities.
- Slashed costs. AI agents automate key business workflows, allowing companies to minimize costly human errors and enable significant operational cost savings. On top of that, AI agents can automatically scale to address growing workloads, sparing you overhead costs for a staff increase.
- Innovation enablement. With advanced, fast analytics generated by AI, you can identify new market trends, user behavior patterns, etc. to perfect decision-making. AI agents can also assist you in developing new products and services for getting a competitive advantage.
Key Types of Agents in Artificial Intelligence
Based on your business and industry needs as well as an AI agent’s intelligence level, decision-making capabilities, and interaction with surroundings, you can choose among the following types of agents in artificial intelligence.
Simple Reflex Agents
Being the most basic type, simple reflex AI agents leverage their current observable environment and operate only on predefined condition-action rules, without taking into account past experiences or possible consequences.
Based on the ‘if-this-then-that’ logic, such AI agents have a performance element that processes input from sensors to perform an action through an actuator in simple, fully observable, and static environments. Among the common use-cases are:
- Thermostats that use temperature analysis to switch on / off
- Automatic doors underpinned by sensors to detect a motion
- Vacuum cleaners equipped with bump sensors to avoid an obstacle
- Automatic street lights that operate on light level thresholds
- Email spam filters that work based on simple keyword matching
- Factory quality controllers, including weight, dimensional, and optical inspections
The value of simple reflex agents especially expands when they pair up with other AI agents, forming multi-agent systems such as smart city traffic management, automated warehouse operations, or enterprise-grade IT service management. So if your business revolves around manufacturing, quality control, real-time monitoring, or IT operations, a powerful simple reflex agent will become a helpful co-worker.
Model-Based AI Agents
A more sophisticated version of a simple reflex system, a model-based AI agent has an internal module that not only uses current perceptions, but also tracks the environment’s past states to make decisions and predict future changes. This allows them to effectively function in partially observable or dynamic environments, where the context needs to be remembered:
- Dynamic pricing systems are AI agents used by e-commerce platforms like eBay or Amazon to analyze user demand, competitors, and previous purchasing patterns to dynamically adjust product pricing. In apps such as Uber, these agents adjust prices in real-time based on demand, time of the day, and weather to maximize revenue.
- Customer chatbots make the most of their short-term memory to memorize conversation contexts and provide more tailored and relevant responses.
- Remote patient monitoring. Such industry-specific agents are able to track data from glucometers, heart monitors, and other wearables, compare it against a patient’s historical baselines, and activate proactive alerts about potential health issues.
- Trading AI agents are fed with data from their internal models (including market trends, financial news, and historic information) to forecast price movements and execute trades with minimized risks.
Summing it up, model-based AI will be perfectly suited for your business if you work with historical data and predictive analytics for more powerful system performance and enhanced decision-making.
Goal-Based AI Models
Goal-based AI agents operate by selecting actions to pursue a particular goal. The sequence of actions that are most likely to help reach the goal is defined through advanced planning and reasoning algorithms. Here are some use-cases of goal-based AI agents:
- GPS navigation systems are set to reach a particular destination. In this case, the AI agent leverages planning algorithms like Dijkstra’s or A-Star that analyze different roads and turns to build the optimal route.
- Inventory management can also be driven by AI. The agent analyzes projected usage rates to plan reorder actions. This way, the goal of ensuring sufficient inventory and preventing stockouts is met by a particular date.
- Logistics scheduling agents generate a complex, multi-step schedule of tasks to efficiently deliver goods. To reach the objective of minimizing costs and maximizing on-time deliveries, the AI agent continuously monitors the environment for disruptions (like traffic jams) and replans actions in real time.
- Robotic surgery assistants help human doctors perform high-precision actions and adjust pre-approved surgical plans in real time through its closed-loop system by underpinned sensor feedback.
- Gaming. In this sphere, goal-oriented AI agents are used to build realistic, intelligent behavior for non-player characters by performing tasks like ‘attack the enemy’, ‘collect items’, ‘find the gun’, etc. (through pathfinding and planning algorithms).
As you can see from real-world examples, goal-based AI agents will perfectly fit businesses, where performing clear tasks (with real-time adjustments) is crucial, like in robotics, logistics, and autonomous vehicles building.
Utility-Based AI Agents
As opposed to goal-based AI systems, utility-based agents not only achieve a particular objective, but also consider a variety of possible outcomes, assign a pre-defined utility function to each, and identify the most ideal course of action. This is particularly important in dynamic environments where binary goal-based decisions aren’t sufficient, i.e. multiple tradeoffs are involved.
- Finances where profit maximization and risk minimization are key, utility-based AI agents can help allocate capital across different assets, considering the company’s risk tolerance, market uncertainties, and other complex factors.
- Digital marketing. By using its ad-bidding utility function, the AI agent is able to balance the cost of the pay-per-click bid, calculate the expected ROI of every possible bid in real-time auctions, and choose the optimal combination for maximizing your campaign’s profitability.
- Medicine. AI agents’ utility function gauges factors such as recovery probability, treatment cost, adverse effect risks, etc. to provide physicians with the optimal treatment plan for both the patient and the hospital.
- Human resources and talent acquisition. Empowered by a utility function, AI agents use screening tools to analyze potential candidates, factoring in multiple criteria. A higher utility can be assigned to a candidate with the proven niche experience even if their salary expectations are higher than average. This results in enabling long-term value for a firm.
Learning Agents
This type of an AI agent continuously learns the feedback (experiences, data) from complex, ever-changing environments, updates its behavior, and improves its performance over time. Such agents can leverage different learning methods, including:
- Supervised learning presupposes leveraging labeled data to make predictions.
- Unsupervised learning includes finding certain patterns in unlabeled data.
- Reinforcement learning means finding the optimal strategies through trial-and-error interactions, while receiving rewards for correct actions and penalties for incorrect ones.
The ability of agents to learn from interactions and uncertain situations, while combining different learning methods, allows businesses to benefit in the following fields:
- Content recommendation platforms. Fed with data about viewer browsing history, preferences, and typical behavior, learning AI agents can notably improve predictions, enabling hyper-personalized recommendations that adjust over time. For example, such mechanisms lay behind platforms like Spotify and Netflix.
- Autonomous vehicles (like Tesla) capitalize on the internal model of the learning agent to analyze road conditions, traffic patterns, and pedestrian movements based on sensors (radars, cameras, LiDAR, etc.). This allows them to predict outcomes, choose the optimal driving behaviors through trial and error, thus perfectly dealing with previously unknown situations, adapting to adverse weather conditions, etc.
- Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa leverage natural language processing coupled with ongoing interactions with humans to learn their preferences, commands, and accents. This is key to provide accurate responses, give personalized advice, and perform various tasks.
- Fraud detection systems. As scammers constantly change tactics and create more sophisticated attacks, learning AI agents adapt to recognize, understand, and prevent evolving fraudulent patterns.
- Online education is another sphere where AI agents find their feet. They create personalized learning paths and programs for students, adjusting difficulty and pace according to a person’s individual progress and learning style.
AI Agent Implementation with Aetsoft
Choosing the most suitable AI agent that would correspond to your specific business needs is half the way. At this stage, consider aspects like:
- Complexity level (agent autonomy)
- Specific use cases based on your niche
- Technical capabilities (performance, scalability, interoperability)
- Ethical aspects, including bias, transparency, security, compliance
- Cost and ROI, vendor support
- User experience and adoption
The lion’s share accounts for AI agent implementation. Experts with multi-year experience in Artificial Intelligence consulting and development, Aetsoft has got your back with:
- Full-fledged AI agent integration
- AI agent customization
- Private large language model development
- AI agent maintenance and support