Blockchain applications in cybersecurity
-
DNS servers
-
Private messaging
-
Hardware
Use case 1. Decentralized DNS

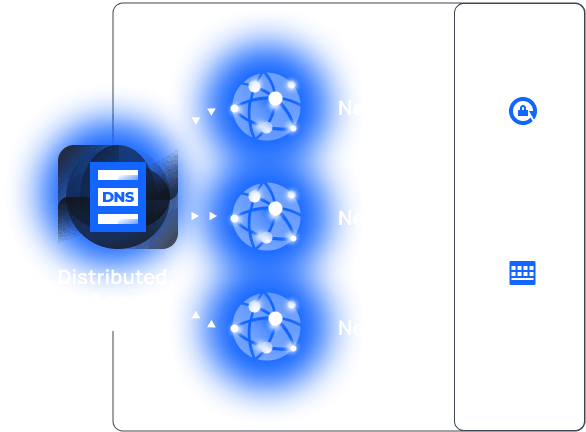
Currently
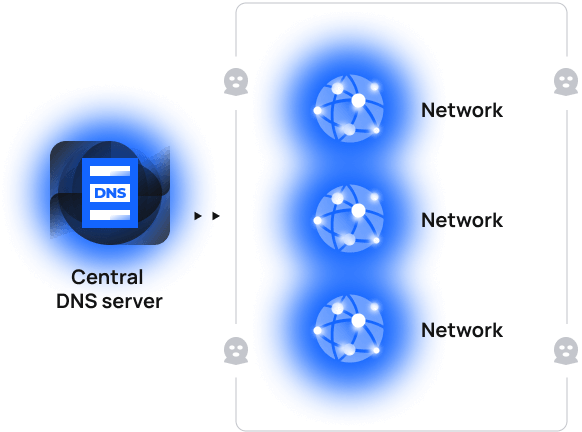
Centralized DNS servers, though accelerate networks, make those vulnerable to DDoS and other attacks because of single access points to these networks.
With blockchain
Set up a distributed, blockchain-based DNS server, with connections to each related network cryptographically-protected.
Use case 2. Secure private messaging

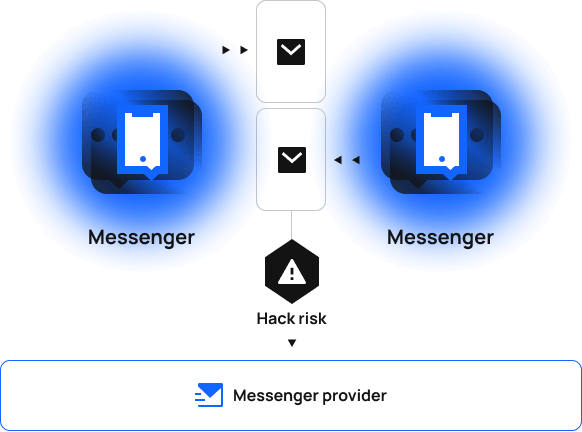
Currently
Private messaging between users often turns out to be not private at all; when messages are visible to messenger providers, hacks might be inevitable.
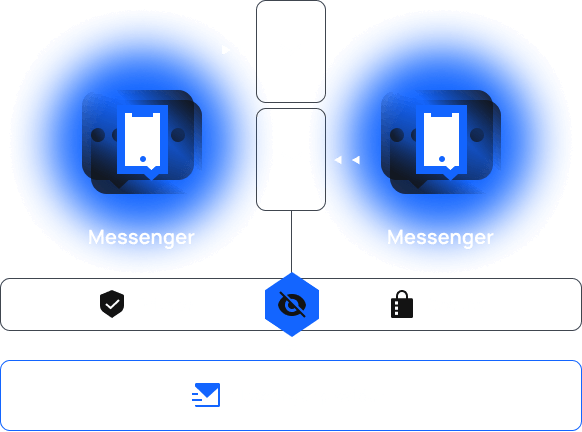
With blockchain
Secure communication channels via blockchain encryption to make them truly private! No more unauthorized access; only sender and recipient are eligible to view their message history.
Use case 3. Hardware authenticity

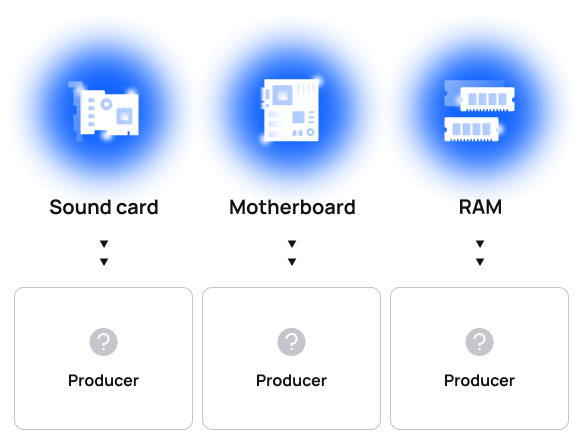
Currently
Often fragmentary nature of manufacturing records and inconsistent record-keeping in general leaves distributors and end customers unaware of the origins of individual hardware items — if not all of them.
With blockchain
Provide consistency and transparency across your manufacturing records by keeping those in a universal blockchain database, immutable and forgery-proof.