Blockchain applications in supply chain
-
Proof-of-provenance
-
Detecting contamination
-
Secure transactions
Use case 1. Proof-of-provenance

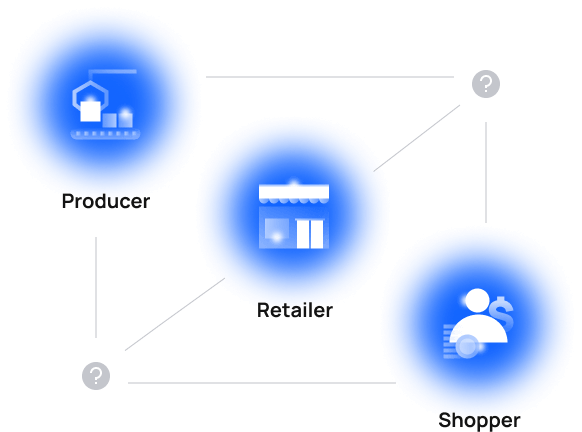
Currently
Data fragmentation leads to inadequate provenance tracking in supply chains, where shoppers are unaware of the quality of products they purchase.
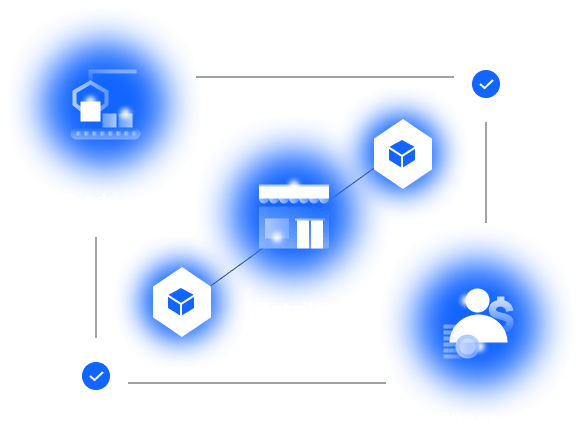
With blockchain
Blockchain keeps a permanent record of all parties involved in a supply chain, with the origins data transparently visible to consumers.
Use case 2. Detecting contamination

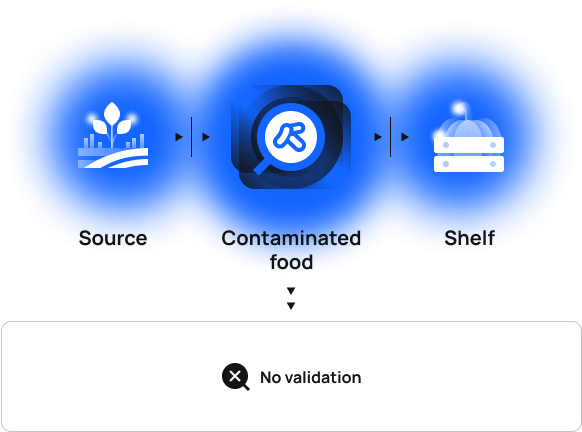
Currently
Insufficiently regulated nature of today’s supply chains makes room for contaminated foods paving their way to shop shelves — if not validated promptly.
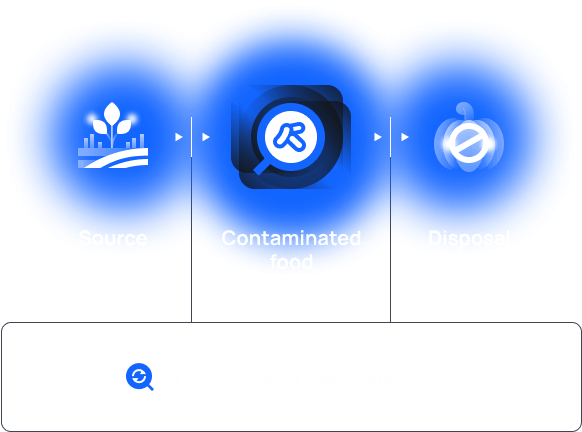
With blockchain
Blockchain establishes a network where all supply chain parties verify food quality against mutually agreed quality standards from the moment of origination.
Use case 3. Secure transactions


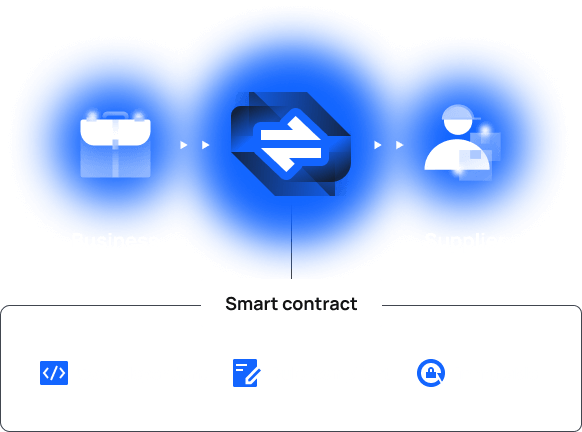
Currently
Deals between businesses and suppliers are usually not backed by compliance guarantees; parties might not pay in due time, or fail to fulfill payment commitments.
With blockchain
With blockchain-enabled smart contracts, supply chain partners can conduct deals without even trusting each other; code-dependent smart contracts will trigger actions strictly upon meeting agreed terms.